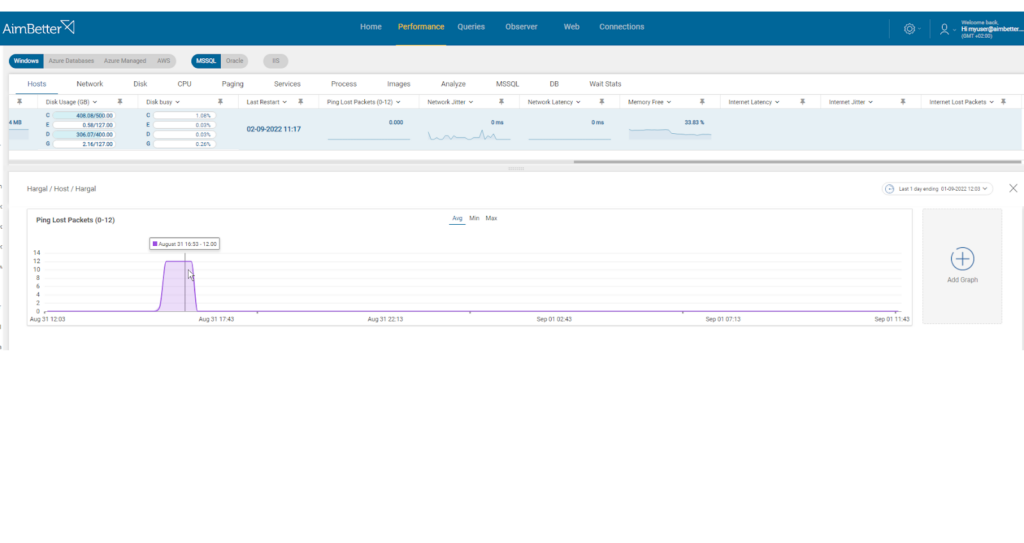
AimBetter communicates every 5 seconds with the server via a ping command. The success of the ping and the time taken (latency) are monitored to assess the health of network connections to the server. Note that this metric deals only with communications between the server and AimBetter, not between the server and users
Find out how you can save hours of work when investigating the root cause of this issue.
Symptoms:
The server is not responding or missing packets.
Impact: Medium
Lost packets alert indicates that communications with the SQL server either get no response or only partial response. As well as delays experienced by users, there is a possible loss of data. If the server is not responding, all traffic between the user and the server will halt. If missing packets, there will be an effect on application functionality and performance. The main effect on performance comes from packet retries which can significantly load the level of network traffic. As well, queries will have to wait for data, thus increasing the possibility of blocks, and deadlocks, and will elevate page file activity as buffer pool space is locked.
Expected behavior :
The server should respond to every ping. AimBetter will raise an alert if 12 pings in sequence fail
Possible causes:
1- Network load Priority: Medium
When the volume of network traffic exceeds the capacity of the network infrastructure to handle it, the network load might be high. When this happens, packets may be dropped or lost in transit.
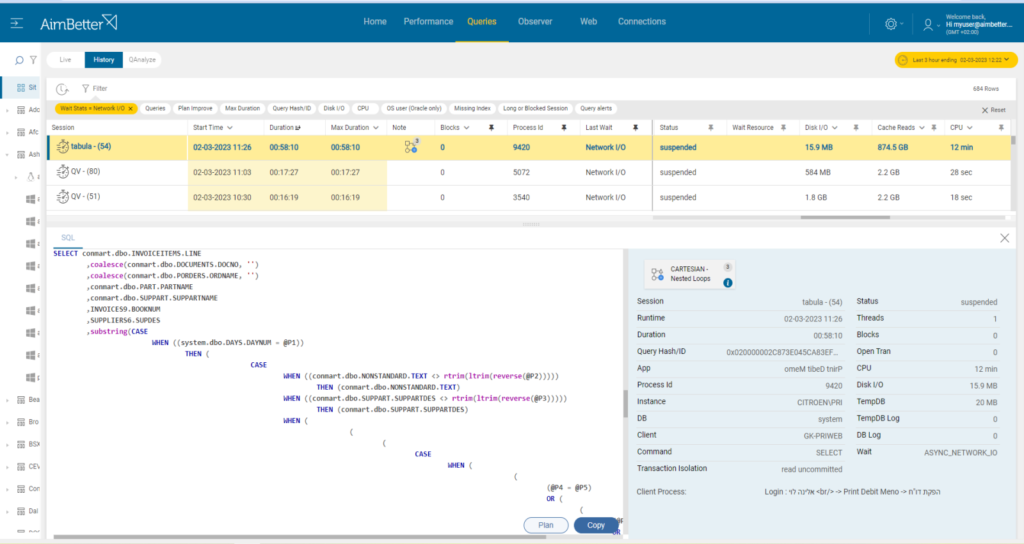
Problem identification
Check current traffic and which applications use most of it.
- Using a network monitoring tool, you should check how much traffic flows through your network and which applications or devices use the most bandwidth. Notice that most monitoring tools help pinpoint when a problem starts, but you can’t compare time frames.
- Review your network logs to see if there are any unusual patterns. This might take considerable time.
- In Linux environments, there are diagnostic tools such as “netstat” or “ss commands” which can display network connections and statistics, including information about packet loss. In addition, Linux systems log various network-related events and warnings, which can be useful for investigating the root cause.
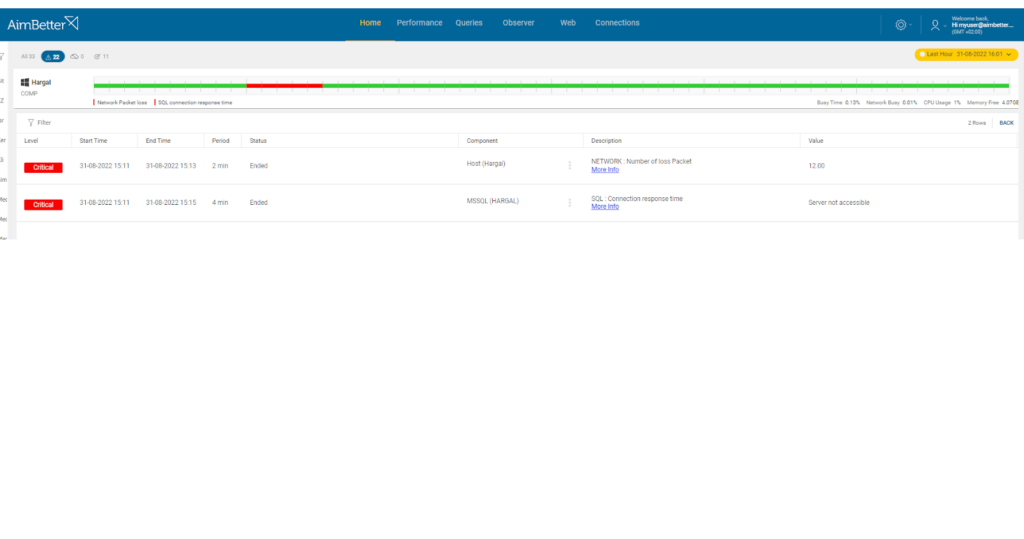
Our solution raises an immediate alert once there is a network problem.
With AimBetter, you can easily investigate what happened next to the event.
Recommended action :
Check network traffic loads with a network analyzer. If possible, move high-volume traffic (e.g, remote storage, backups) onto a secondary network.
2- Incorrect network settings Priority: Medium
Look for our network utilization article regarding inefficient network structure.
3- Large data transfer load in the network. Priority: Medium
When data is transmitted across a network, it is broken down into packets that are transmitted individually and then reassembled at the destination. If the volume of data transfer is too large, it can potentially result in packet loss.
Problem identification
Actively follow the data transmission amount in parallel to packet loss.
- Using a network monitoring tool, you should check how much traffic flows through your network. Take into account that most monitoring tools help pinpoint when a problem starts, with which you can’t compare time frames.
- Measure the amount of bandwidth being used during the data transfer. When it’s large, it might cause packet loss. You probably have to use a monitoring tool for that.
- Monitor and analyze the data transfer load in parallel to packet loss recurrence. Initiate a test for that issue to identify the maximum data transfer rate possible using the network. You will probably need the help of an expert IT professional.
- In Linux environments, look at network logs related to network events and warnings. Follow up on network statistics and connections while looking for diagnostics. Using “traceroute” commands can help identify the route packets take to reach a destination and highlight network hops where packets are being dropped.
Our solution raises an immediate alert once there is a network problem.
You can easily see what happened in parallel to this event.
Recommended action :
If possible, move high-volume traffic (e.g., remote storage, backups) onto a secondary network, or reschedule to periods of low SQL demand
In addition, you should increase the network bandwidth and correction mechanisms to optimize the transfer process.
4- The connection is lost Priority: Medium
Once the connection is lost, it will immediately cause a packet loss. In cases of complete disconnection, when 12 packets have been lost in succession.
It might happen because of a network failure (router, bridge, other hardware) or a server crash /power-off.
Problem identification
Check the physical environment. Look for network failures or check for a shutdown of the server.
- Look for network latency or failed hardware. You can read more in our Network Latency article.
- If the firewall or security settings are too restrictive, they can block network traffic, causing lost connections and packet loss. You will need the help of an expert IT to check it.
- Check if the server is up. For that, you must have the correct permissions.
Using our solution, you immediately get an alert once a network packet is lost.
Looking at our system logs and tracked issues, you can know what happened next to that event.
Recommended action :
In case of a server crash, restart and investigate the cause of the crash. In case of network failure, replace faulty components and restore network functionality.